Research Summary
The report discusses the scalability solutions for Ethereum, focusing on Layer-2 solutions such as Optimistic rollups and zkEVM. It explores the role of sharding, the centralization of current rollups, and the challenges for zero-knowledge rollups. The report also delves into the Optimism Bedrock architecture, the impact of EIP-4844 on reducing gas costs, and the predicted migration of capital from Ethereum Layer-1 to Layer-2 networks. It further examines the potential for decentralizing Layer-2 sequencers, the creation of appchains, and the expected shift of developers to Optimistic rollups.
Key Takeaways
Scalability Solutions for Ethereum
- Layer-2 Solutions: The report discusses Layer-2 solutions such as Optimistic rollups and zkEVM that address the scalability trilemma by executing transactions on an external computational layer with the same security guarantees as the underlying Layer-1. Sharding, or partitioning the Layer-1’s state into shards, is one approach to tackling scalability and reducing computational resource requirements.
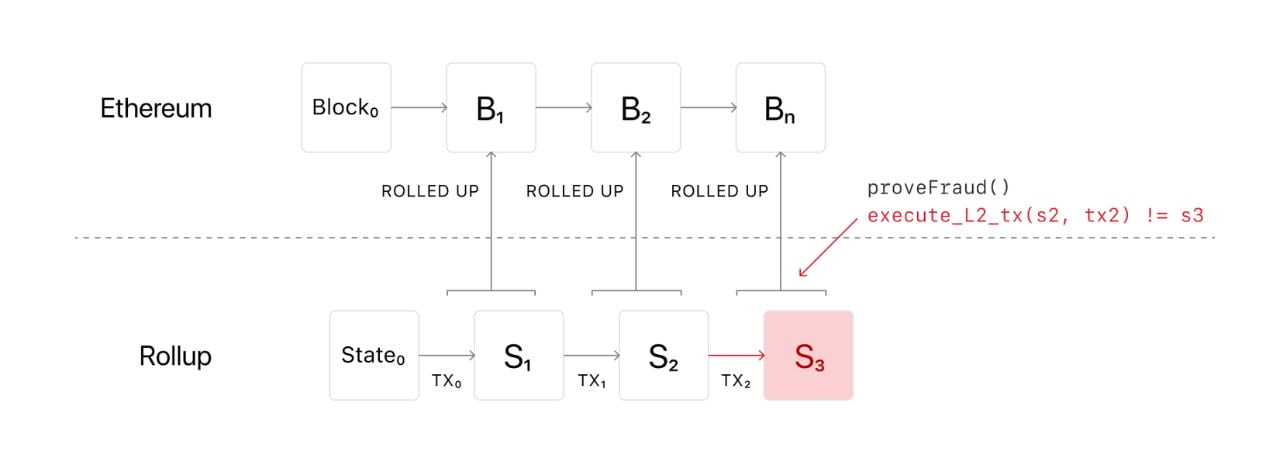
- Optimistic Rollups: Optimistic rollups batch transactions together and provide a proof of the state transition, reducing the amount of bytes needed for transaction validation on Ethereum’s Layer-1. Transactions are assumed to be valid with a 7-day contestation period where actors can contest a state update using fault proofs.
- Zero-Knowledge Rollups: Zero-knowledge rollups provide verifiable proofs of state transitions, while optimistic rollups assume state transitions are valid unless proven incorrect through fraud proof resolution. The primary challenges for zero-knowledge rollups are EVM equivalence and proof times/costs.
- zkEVM: The zkEVM aims to fully integrate the EVM into an arithmetic circuit for zero-knowledge proofs, eliminating the need for custom arithmetic circuits for each program. It requires novel cryptographic techniques and optimized hardware to decrease proof times.
- Migration to Layer-2 Networks: Capital is predicted to migrate from Ethereum Layer-1 to Layer-2 networks, with EIP-4844 accelerating the exodus of capital to Optimistic rollups. It is projected that 70% of Ethereum’s Layer-1 TVL will migrate to a Layer-2 within the next 5 years.
Optimism Bedrock Architecture and EIP-4844
- Optimism Bedrock Architecture: The Optimism Bedrock architecture introduces a modular stack approach to Layer-2 rollups, allowing for easier system design and future iterations. The consensus layer in the Bedrock architecture acts as the data availability layer, ensuring the security of the system by allowing attesters to reconstruct state transitions.
- EIP-4844: EIP-4844 is an Ethereum Improvement Proposal that aims to reduce Layer-2 transaction gas fees by a minimum of 20x by introducing a new transaction type called a “blob-carrying transaction.” The implementation of EIP-4844 is seen as the catalyst for the realization and mass adoption of the Ethereum rollup-centric roadmap.
Decentralization of Layer-2 Sequencers and Creation of Appchains
- Decentralization of Layer-2 Sequencers: Layer-2 sequencers in their current form are highly centralized. Progressive decentralization of the sequencer can be achieved through a proof-of-stake mechanism, where users stake the native L2 token and receive rewards for honest behavior.
- Creation of Appchains: Layer-2 modularity allows for the creation of appchains, where projects can deploy their own chains that inherit the sequencer of the original Layer-2. Appchains can have cross-chain atomic transactions, enabling interoperability and avoiding performance issues caused by other DApps on Ethereum’s Layer-1.
Shift of Developers to Optimistic Rollups
- Migration of Developers: Developers are likely to migrate their existing DApps or create new DApps on Optimistic rollups to lower gas costs for users. Over the next three years, the majority of on-chain activity is expected to shift to Optimistic rollups, presenting an opportunity for significant value capture as liquidity and on-chain activity move away from Layer-1 to a more cost-effective transaction environment.
Actionable Insights
- Exploring Layer-2 Solutions: Stakeholders should explore Layer-2 solutions such as Optimistic rollups and zkEVM to address scalability issues. Understanding the benefits and challenges of these solutions can help in making informed decisions.
- Understanding the Impact of EIP-4844: Stakeholders should understand the impact of EIP-4844 on reducing Layer-2 transaction gas fees. This can help in assessing the potential for mass adoption of the Ethereum rollup-centric roadmap.
- Considering Decentralization of Layer-2 Sequencers: Stakeholders should consider the potential for decentralizing Layer-2 sequencers through a proof-of-stake mechanism. This can incentivize further decentralization and reward honest behavior.
- Exploring the Creation of Appchains: Stakeholders should explore the potential for creating appchains, which can enable interoperability and avoid performance issues caused by other DApps on Ethereum’s Layer-1.
- Assessing the Shift of Developers to Optimistic Rollups: Stakeholders should assess the potential shift of developers to Optimistic rollups. This can present opportunities for significant value capture as liquidity and on-chain activity move away from Layer-1 to a more cost-effective transaction environment.