Research Summary
The report discusses the concept of intent-centric design in blockchain systems, which simplifies on-chain transactions by focusing on the desired outcome rather than the steps required. It highlights the benefits of such systems, including improved user interfaces, better handling of gas fees and slippage, and increased composability. The report also explores the lifecycle of an intent-centric transaction, the role of various actors in the process, and the application of this design in projects like CoW Protocol, CoW Swap, Soul Wallet, and UniswapX. It further delves into the potential applications, risks, and challenges associated with intent-centric design.
Key Takeaways
Intent-Centric Design: A Game Changer in Blockchain
- Revolutionizing Blockchain Transactions: Intent-centric design simplifies on-chain transactions by focusing on the user’s desired outcome rather than the steps required. This approach makes blockchain interactions more accessible to average users and offers sophisticated actors better user interfaces, improved handling of gas fees and slippage, and increased composability.
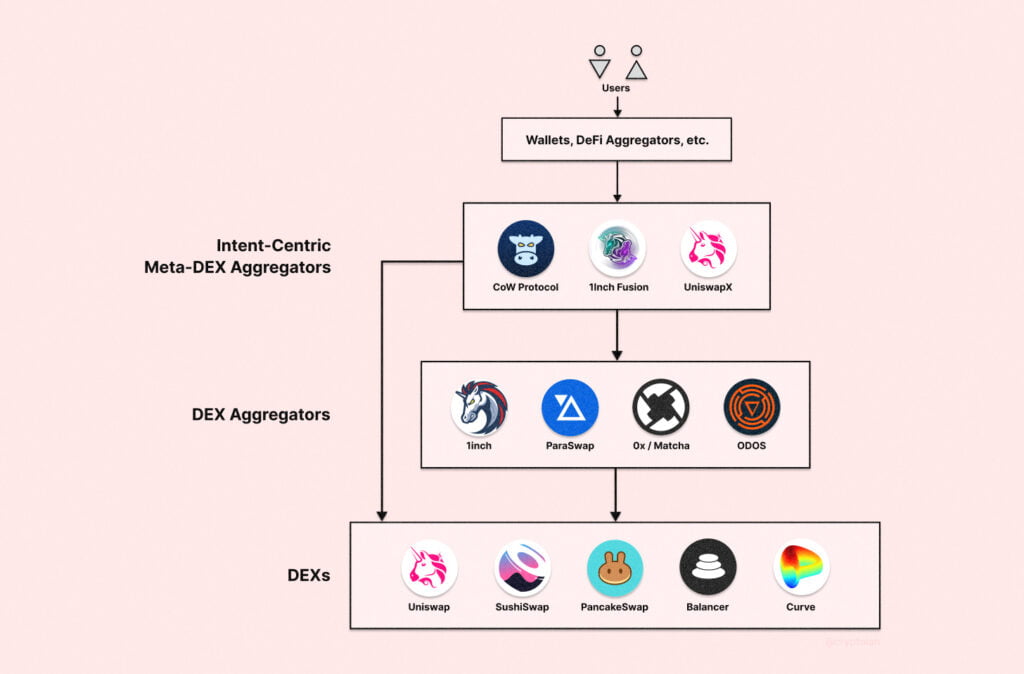
- Role of Various Actors: In an intent-centric system, users submit transactions off-chain, which are then analyzed by MEV searchers for profit opportunities. Solvers compete to provide the best transaction execution and earn fees by aggregating multiple intents into bundles. Block builders select these bundles and package them into blocks for inclusion on-chain.
- Real-World Applications: Early forms of intent-centric design are seen in projects like CoW Protocol, CoW Swap, Soul Wallet, and UniswapX. These projects leverage intent-centric design to provide users with the best realization of their intents, find the lowest prices on trades, offer a user-friendly smart contract wallet experience, and tackle challenges in DeFi.
- Future Potential: Intent-centric design can be combined with AI to personalize and automate investment strategies. It can also be used to connect traditional finance and DeFi, allowing users to convert traditional financial assets into tokenized blockchain assets and utilize them as collateral for DeFi loans.
- Risks and Challenges: Intent-centric design comes with risks and challenges, including the outsourcing of decision-making to third parties, the risk of intentions being misinterpreted, and security threats. To prevent centralization and incentivize good behavior, crypto users should demand system designs that promote transparency and cryptoeconomic incentives.
Actionable Insights
- Exploring the Potential of Intent-Centric Design: Developers and blockchain architects should consider the benefits of intent-centric design, which simplifies on-chain transactions and improves user experience. This approach could accelerate the adoption of consumer crypto applications.
- Addressing Risks and Challenges: To mitigate the risks associated with intent-centric design, architects should build frameworks that discourage malicious behavior and promote transparency. Standardized forms of communication could also help prevent the misinterpretation of user intents.
- Capitalizing on Future Opportunities: The potential applications of intent-centric design in areas like AI, traditional finance, and DeFi present opportunities for innovation. Developers could leverage this design to create personalized and automated investment strategies, connect traditional finance and DeFi, and generate yield on real-world assets.