Research Summary
This report provides an in-depth analysis of Layer 2 (L2) blockchains, their purpose, problems they solve, and their potential market size. It compares various L2s with Layer 1 (L1) alternatives and discusses common L2 architectures. The report also examines the teams behind these L2s and their financials.
Key Takeaways
Purpose and Problem of L2s
- L2s Enhance Scalability: L2s scale L1s by batching transactions on a separate chain and sending them back to L1 for settlement, resulting in lower gas costs and higher throughput. They can also be application-specific, introducing benefits such as granular scalability, finer control over MEV, and developer composability.
- High Transaction Costs on Ethereum L1: Transactions on Ethereum L1 cost up to 980x more than on alternative L1s. This high cost and limited throughput have led to the rise of alternative L1s and the need for Ethereum to scale to retain users.
- L2s as a Solution: L2s solve these issues by batching transactions on a separate chain and sending them back to L1 for finalization. This results in lower gas costs and higher throughput, making L2 gas costs comparable to alternative L1s.
Current Market and Competition
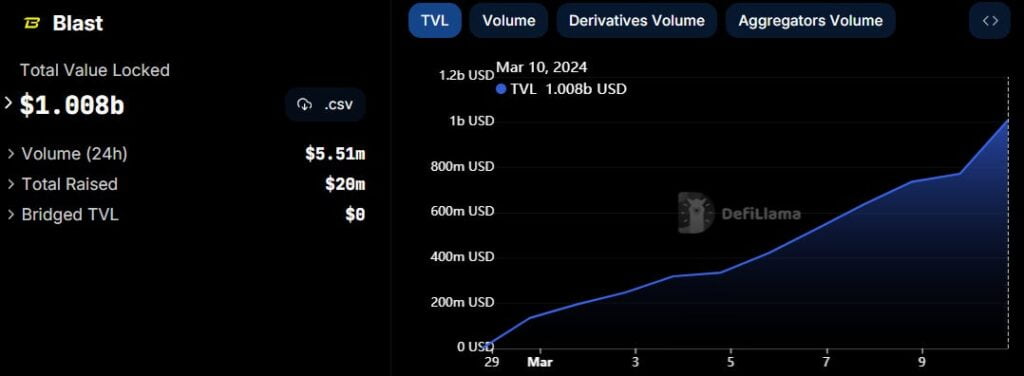
- Increasing Adoption of L2s: Ethereum’s congestion and rising gas prices have led to increased adoption of L2s. The total value locked (TVL) in L2s has grown from $750m to $7b in just three months.
- Market Size and Competition: L2s currently have a 20% market share with 750k-900k daily active users (DAUs). The most popular L2 by DAU count is Polygon, while Arbitrum leads by TVL.
- Types of L2s: There are several types of L2s, including optimistic rollups (Arbitrum, Base, OP Mainnet), zero-knowledge rollups (Starknet, zkSync), and sidechains (Polygon). All offer significantly higher throughput and lower gas fees than Ethereum L1.
Business Model and Financials
- Revenue Model: L2s generate revenue by taking a cut of the gas fees paid by end-users. The remaining amount is used to pay for L1 settlement. L2s optimize gas costs to attract more users, compensating for lower unit revenue through scale.
- Financials: Most L2s currently operate at a loss as they run ecosystem grant programs to bootstrap their ecosystem. On average, L2 developer teams have raised significant VC rounds and allocated a sizable percentage of their cap tables to core contributors and investors.
Actionable Insights
- Investigate the Potential of L2s: With their ability to solve scalability issues and lower transaction costs, L2s present a promising solution for the future of blockchain technology.
- Consider the Market Dynamics: The increasing adoption of L2s and their growing market share indicate a shift in the blockchain market. Understanding these dynamics can provide valuable insights for future strategies.
- Examine the Business Models: The revenue models of L2s, particularly their approach to gas fees, offer interesting perspectives on how blockchain platforms can generate income while attracting more users.